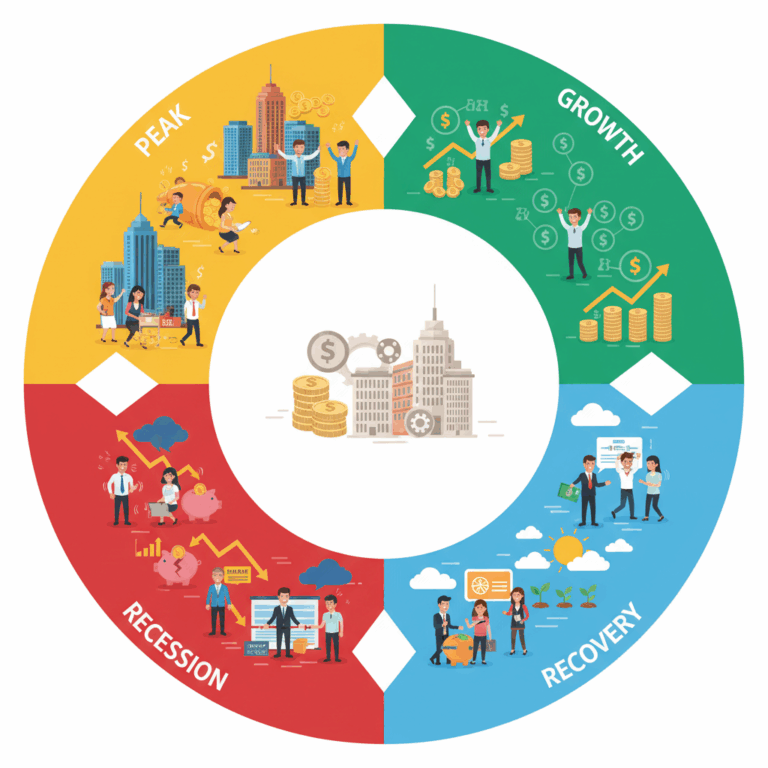
Definition and phases of the economic cycle
He economic cycle It is a recurring pattern that describes the fluctuation between expansion and contraction of economic activity. Over time, economies go through these phases.
Understanding the economic cycle is essential for analyzing how these changes affect employment, production, and people's quality of life. Its main phases are growth and recession.
Concept of the economic cycle
The business cycle refers to the regular fluctuations in economic activity, where periods of growth are followed by slowdowns. It is a natural dynamic in any economy.
These fluctuations affect variables such as production, employment, and consumption, directly influencing a country's financial and social stability.
This concept allows us to anticipate and better understand the causes and consequences of economic changes, facilitating the development of appropriate policies.
Main phases: growth and recession
The phase of growth It is characterized by a sustained increase in production, employment, and consumption. It is a period of economic expansion and opportunities for the population.
In contrast, the phase of recession This implies a slowdown, with a drop in production, investment and an increase in unemployment, negatively affecting confidence and income.
Understanding these phases helps to visualize how the economic cycle influences society, affecting both job stability and general well-being.
Characteristics of the growth phase
During the phase of economic growthProduction and employment increase considerably. This period reflects expansion and dynamism in the labor market.
Growth drives the economy, generating more job opportunities and promoting a favorable environment for investment and business development.
Increased production and employment
Increased industrial and service production is key during the growth phase. Companies expand their operations to meet increasing demand.
This leads to an increase in the hiring of workers, reducing unemployment rates and improving job stability in various sectors.
Increased production also fosters innovation and technological development, facilitating a positive cycle of economic progress.
Increased consumption and wages
Increased employment leads to growth in wage income, which raises the purchasing power of families and, consequently, the consumption of goods and services.
This cycle favors domestic demand, encouraging companies to continue investing and increasing their supply, which benefits the entire economy.
Higher wages and greater access to credit strengthen consumer confidence, generating a positive and sustained effect on the market.
Improvement in quality of life
The combination of increased employment, wages, and consumption contributes to an improved quality of life for the population. An increase in social and personal well-being is observed.
Families gain access to better services, education, and health, which boosts social development and reduces economic inequalities.
Interesting fact
Quality of life improves not only with higher incomes, but also with job stability and access to social benefits, creating a favorable context for sustainable growth.
Social impacts during the recession
The phase of recession This generates profound social consequences that affect both individual well-being and the overall economic structure. This stage is critical for the population.
During a recession, job and economic opportunities decrease, which has a visible impact on the standard of living and financial stability of many families.
Decline in investment and production
During a recession, a significant reduction in business investment is observed due to uncertainty and lower market demand. This slows economic activity.
The drop in production affects all sectors, generating a domino effect that reduces the supply of jobs and limits the resources available for wages and development.
This decline also reduces the capacity for future growth and hinders immediate economic recovery, creating an environment of caution in businesses.
Increased unemployment and reduced income
One of the most visible impacts of the recession is the increase in unemploymentThis increases economic insecurity and reduces the purchasing power of families.
Job loss leads to salary cuts and reduced income, directly affecting quality of life and access to essential goods and services.
This situation generates social and economic stress, hindering family stability and increasing the vulnerability of already affected sectors.
Consequences of the economic cycle on people
The phases of the economic cycle have a direct effect on people's daily lives. Economic growth generates an atmosphere of optimism and opportunities for personal and professional development.
On the contrary, recession brings significant challenges that can affect the well-being and financial stability of families, increasing social vulnerability.
Optimism and growing opportunities
During periods of growth, consumer and worker confidence increases. More jobs are created and incomes rise, which encourages investment in personal and family projects.
This positive environment allows people to plan for the long term, improve their quality of life, and take advantage of new opportunities for education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
Furthermore, a dynamic labor market strengthens social mobility and reduces poverty rates, benefiting society as a whole.
Challenges and risks in recession
In times of recession, uncertainty and fear of unemployment increase, generating stress and anxiety among the population. Reduced income limits consumption and the ability to save.
People face the possibility of losing their jobs or seeing their salaries reduced, which negatively impacts their quality of life and access to basic services.
This context forces many families to adjust their budgets and seek alternatives to maintain their well-being, increasing social inequality and economic insecurity.